
These days, web applications are of utmost importance in business and innovation. These technologies simplify processes, improve client interaction, and foster creativity. As an entrepreneur preparing to launch the next big idea, a developer willing to sharpen your skills, or a business executive needing to improve the workflow within the company, this manual focuses on the web applications market in 2025. You will uncover the importance of web apps, how they are developed, the recent trends in their development, and the problems you need to address.
What Are Web Applications?
Web applications (or web apps) use interactive techniques that permit the user to communicate directly with software systems through web technologies like HTML, CSS, and Java software foundation. Unlike sets of information in a traditional website, a web application gives prospects or allows users the capability to perform incremental as well as value-creating functions such as addition, modification of data, and storage of output (Input).
Here’s the key difference:
- Website: Focuses predominantly on output—E.g., News portals, blogging sites, etc.
- Web Application: Having a predominant focus on input. For example, Google Docs enables document creation, editing, and sharing.
Web apps are programs users can run directly from their web browser and utilize backend and front-end technologies. The development of computers and the internet led to web applications that are highly interactive, efficient, and scalable. Such applications can run seamlessly on almost any device that has internet connectivity.
The Evolution of Web Applications
The web applications we know today have evolved from the simple dynamic sites of the early 2000s. Some of the improvements include:
- Single-Page Applications (SPAs): Interactively performed with dynamic content updating. Therefore, refreshing the page is not required.
- Progressive Web Applications (PWAs): Applications that are responsive and capable of functioning like native applications (e.g., running offline and being able to send out push notifications).
- AI-Powered Web Apps: These applications use Artificial Intelligence to automate, personalize, and make complex decisions easily.
Web applications should not be considered optional for businesses, as they are now necessary.
How Web Applications Are Built
Creating a web application involves blending several technologies and architectural components. At its core, all web apps rely on:
- Front-end: User interface and presentation layer. It is translated using HTML and css, together with javascript libraries and frameworks like React and Vue.js or Angular.
- Backend: This component is in charge of your data processing, server logic, and database communication. Options here include Python, PHP, and Node JS.
- Database: Responsible for storing, retrieving, and managing data relevant to the application being built. Some examples include relational database management systems like MySql and PostgreSQL or non-relational systems like MongoDB.
- Hosting: After development, web apps are hosted through cloud services (e.g., AWS, Google Cloud) or local infrastructure.
Popular Web Architectures
- Model-View-Controller (MVC): Separates data, UI/UX, and logic for better organization and scalability.
- Single-Page Application (SPA): Focuses on loading dynamic content without refreshing the page, which is ideal for fast user experiences.
- Microservices Architecture: Breaks tasks into independent services, simplifying scalability and development.
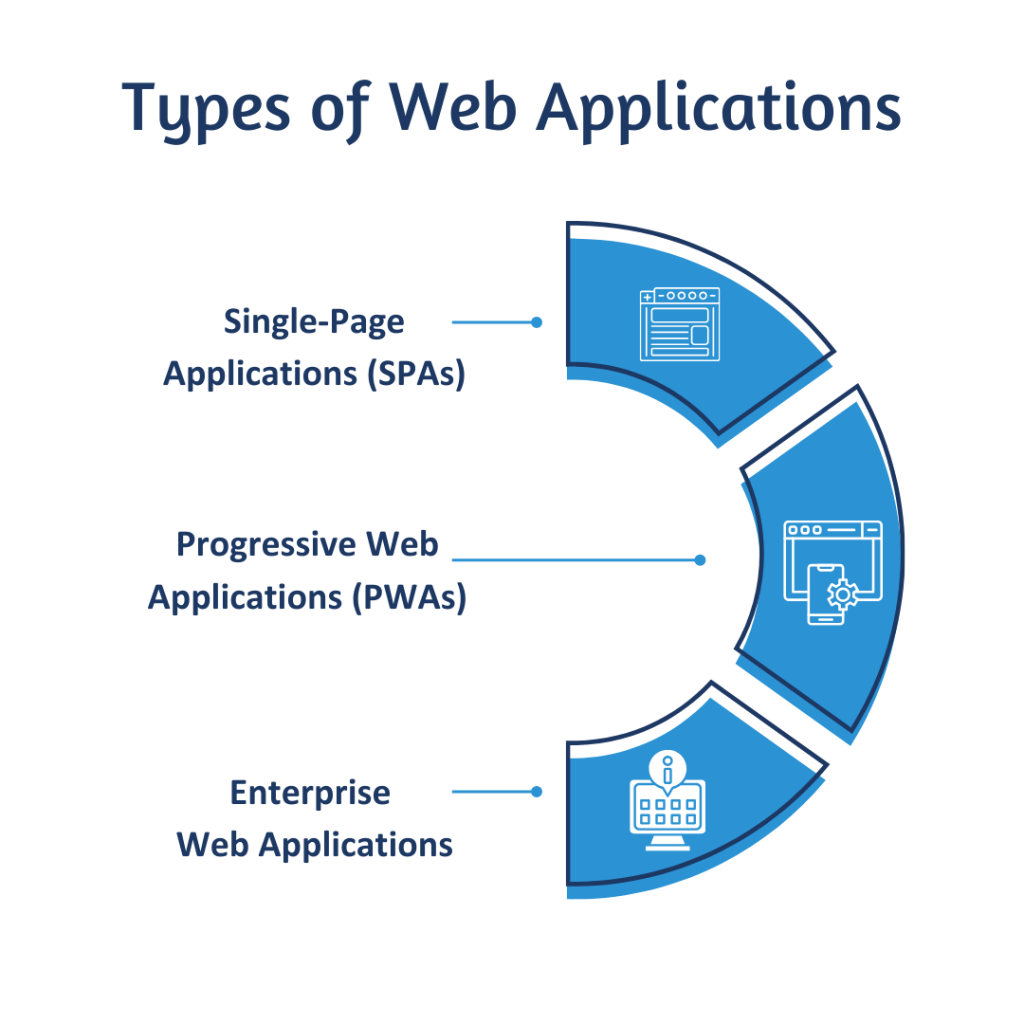
Types of Web Applications
Web applications fall into various categories based on their functionality and user experience. Below are the most popular types:
Progressive Web Applications (PWAs)
PWAs merge a native app and a website. These apps can be installed on a device, work offline, and even send push notifications. There is no need to download anything from the app store since PWAs enable users to have an app-like experience instantly on the browser.
Single-Page Applications (SPAs)
With SPAs, services such as Gmail load a single HTML file, which can fetch new content. Dynamic updating content reduces load times and streamlines navigation. However, advanced front-end frameworks are now necessary.
Enterprise Web Applications
Designed for businesses, enterprise web apps aid in managing operations, providing analytics, and scaling processes. Salesforce is a prime example, enabling effective CRM management for global enterprises.
Popular Web Application Examples
Here’s a list of groundbreaking web apps showcasing different capabilities:
- Mailchimp – automates marketing and email campaigns.
- Google Docs – facilitates document creation and editing with multiple users.
- Notion – tackles project management, notes, and collaboration in one app.
- Airtable – offers a cloud-based database and online workflow management.
- Xero – offers accounting services for small businesses.
- Salesforce – the leader in customer relations management systems
- Slack – advanced messaging for teams
- Canva – graphic design tool accessible to all
- Trello – organizes projects and assigns tasks efficiently.
These examples demonstrate the diverse utility of web applications—spanning marketing, productivity, and collaboration.
Why Develop a Web Application?
When deciding whether to develop a web application, it’s helpful to consider your alternatives. Here are a few options:
- A website
- A native app
- Local software
- Doing nothing at all
Now, let’s explore why a web application might be the smartest choice, especially compared to desktop software or native mobile apps.
Faster Deployment
With web applications, deployment is simple and rapid. Unlike mobile applications, there are no tedious review processes involved. For instance, submitting a native application to the Apple App Store or Google Play can take weeks. Not to speak of the proprietary frameworks like Xamarin for Android and Swift for iOS, which severely limit your choices. With a web application, you only need to share a URL, and your app will be available in seconds.
Easy Access
Since web apps are accessible via all browsers, users can easily access your tools on phones, desktops, and tablets without downloading anything. Employees can use pieces of equipment whether they are working from the office or off-site and still be able to get access to the necessary tools. Customers also benefit since they can access the services using any device, guaranteeing a fantastic experience.
Enhanced User Experience
Mobile applications used to dominate the tech industry; however, web applications are more popular among users today. Installing new applications, managing their screens, and monitoring battery consumption is tiresome for people. Unless they wish to use a native app for a good reason, web apps have made their life easier by functioning independently. Most users prefer an uncomplicated and straightforward solution, which web apps provide.
Economical in Terms of Development
Web applications are typically less expensive and take less time to build than native apps and desktop software. There is no need to learn new proprietary software, undergo tedious vetting, or make installation package files. Furthermore, web app developers tend to use time-saving frameworks and libraries. There has never been a better time to build web apps with the increasing use of low-code technology.
Undoubtedly, web applications provide unparalleled convenience, efficiency, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, which makes them the best option for businesses.
Advantages of Web Applications
Why should businesses consider investing in web apps? Here are the key benefits:
1. Accessibility
Web apps are accessible anywhere with an internet connection, allowing seamless device interactions.
2. Cross-Platform Compatibility
A single web app functions uniformly across different operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux) and devices (laptops, tablets, phones), reducing development time.
3. Scalability
Easily add features or handle larger user bases without significant reworks.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
Developing and maintaining web apps is often more affordable than native applications, as updates are applied server-side without requiring user downloads.
5. Ease of Maintenance
Developers deploy updates or bug fixes centrally, ensuring all users benefit simultaneously.
6. Improved Collaboration
Web apps like Slack and Google Workspace enable real-time collaborations, boosting productivity.
7. Enhanced Security
Modern encryption protocols and cybersecurity measures ensure robust security frameworks to protect user data.
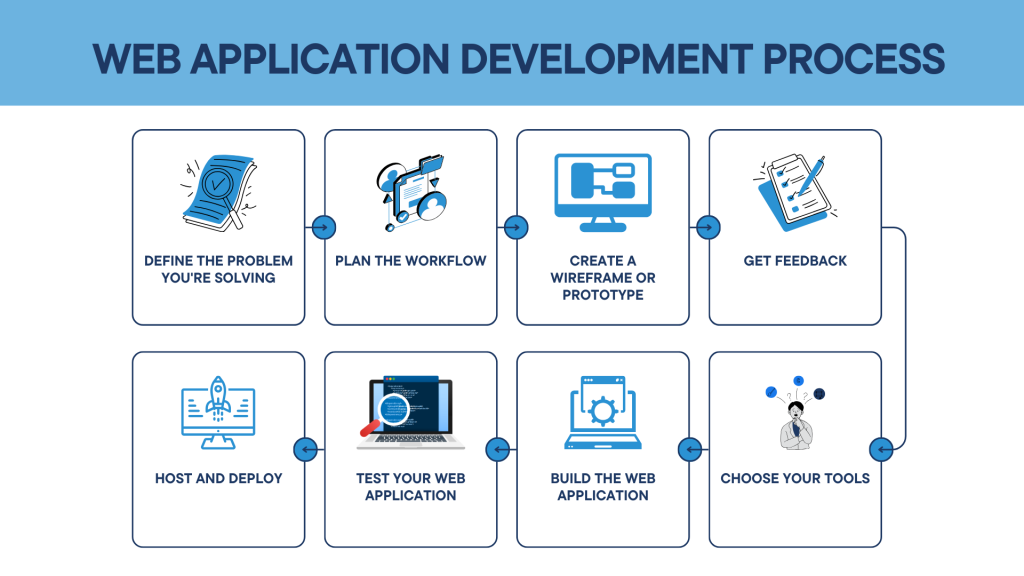
Web Application Development Process
Building a web application involves several key stages. Below, I’ve outlined the essential steps to guide you through the process.
Here’s a quick summary of the eight steps involved in creating a web app:
1. Define the Problem You’re Solving
This is the foundation of your project. Clearly defining the problem gives you a clear direction and shapes the solution.
2. Plan the Workflow
Once you have your solution, map out how it will function. What needs to happen in your web app to solve the problem effectively?
3. Create a Wireframe or Prototype
Turn your workflow into a visual wireframe. This helps communicate your idea to potential users and stakeholders.
4. Get Feedback
Share your wireframe with potential users, gather Feedback, and refine the design until it aligns with their needs.
5. Choose Your Tools
Select the right tools, frameworks, and platforms for your web app. Don’t just go with popular choices; consider what fits your project best. For example, a simple to-do app doesn’t need the complexity of Django and React.
6. Build the Web Application
- Database: Describe the types of data to be saved and the format in which it will be saved. Then, build your database.
- Frontend: Construct the user interface that corresponds to your wireframe, complete with HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and a frontend framework such as React or Vue.
- Backend: Create the backend that takes care of the logic and processing (e.g., authentication, CRUD operations, database communication).
7. Test Your Web Application
Testing should be continuous. Conduct functionality, usability, security, and performance tests within the development phase. User experience can be maintained with both manual and automated user interface testing.
8. Host and Deploy
After you’re set, you can now host your web application on a cloud provider like AWS/Azure; make sure to deploy using continuous integration (CI) tools. You can also set up securing your domain as well.
Learn More: Digital Marketing for Startups: Strategies for Success
Key Elements of Web Application Development
For the web app to operate successfully, it is pertinent that one understands its components. These include:
Database
The database has all the pertinent information regarding the web app. Most applications have relational databases like MySQL or Postgres, but a few do have NoSQL versions to cater to unstructured information, such as MongoDB. It is the responsibility of the database to ensure that there is information for the web application and it is functional.
Application Server
The application server takes care of the application’s business rules along with user logins and the Client’s interaction with the database. It helps in performing tasks that are dependent on the server (using JavaScript, Python, Ruby, etc.) It is hosted on outsourced cloud services or container systems like Docker.
Client (Frontend)
The Client is the part which the user has direct access to. It contains HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which can be augmented with React or Angular. The Client takes care of events from the users, sends requests to servers, receives data, and displays the received data to the users.
API (Application Programming Interface)
The APIs enable web applications to work in integration by defining parameters that aid in the movement of information from the front end, and APIs help apply external services such as payment interfaces or website analysts.
Middleware
Middleware operates between the client, server, application, and database, managing elements of security (authentication), performance optimization (caching), or data transformation. Its modularity increases application maintainability.
Trends in Web Application Development
The future of web apps is dynamic, with key trends shaping the landscape:
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration
AI-powered apps analyze user behavior, automate manual workflows, and offer predictive analytics, making them invaluable for enterprises.
2. Serverless Architectures
By eliminating reliance on physical servers, serverless platforms like AWS Lambda improve cost-efficiency and flexibility.
3. Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
These platforms simplify app creation by empowering non-developers using pre-built components and visual interfaces.
4. Mobile-First Design
With over 55% of web traffic originating from mobile devices, responsive designs ensure stellar user experiences on smaller screens.
5. Microservices Architecture
Breaking applications into modular components allows easier scaling and maintenance. Independent services make upgrades and testing more manageable.
6. Edge Computing
By processing data closer to users (on edge servers), edge computing reduces latency, providing faster and more responsive web apps.
7. Enhanced Security
The rise of cyber threats has pushed organizations to adopt stricter measures, such as vulnerability testing, SSL certificates, and regular patching.
Addressing Key Challenges in Web Applications
Despite their advantages, web apps come with challenges:
- Cybersecurity Risks: Protect user data through encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular audits.
- Performance Optimization: Ensure fast load times with responsive designs, CDN integration, and lazy loading.
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: Test your app across browsers to guarantee uniform experiences.
- Scalability Management: Plan for growth using scalable database solutions or adopting cloud infrastructure.
- Balancing Functionality with UX: Prioritize intuitive designs to ensure users enjoy navigating the interface.
- Accessibility Needs: Use WCAG standards to make apps inclusive for everyone, including individuals with disabilities.
Transform Your Business with Web Applications
Web applications increase industry effectiveness, growth, and customer satisfaction. These tools are essential and beneficial to startups and large corporations alike. From crafting the most innovative SaaS solution to streamlining business processes, web application development has vast prospects. The future is now. Are you prepared to elevate your business?
Check out our web application development services today. Get in touch for a consultation, or share this post with your network to spread the word about what’s new in the web applications market.



